What is A PWM Inverter?
Voltage source PWM inverter drives are the most common type of low voltage inverter drives that are currently in use. The process of obtaining the required frequency involves converting the incoming alternating voltage to DC by means of a rectifier, smoothing the DC in an intermediate DC link with capacitive energy storage, then inverting back to an alternating current.
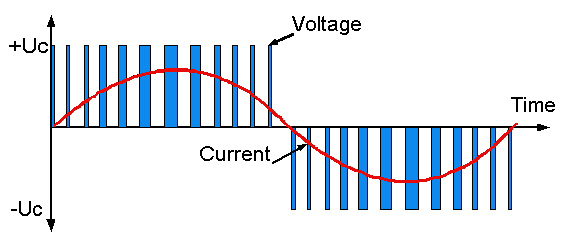
The pulsed output voltage is applied to the motor and the resultant current, modified by the significant motor inductance, consists mainly of the
fundamental sine wave at the required operating frequency with a superimposed low magnitude ripple component based on the switching frequency.
Both voltage and current over one cycle are illustrated in simplified form with deliberately reduced switching frequency in Figure 2 below:
Figure 2 PWM inverter output voltage and current waveforms